of中压力梯度在周期性边界条件中的实现
参考文献:
[1] : https://www.cfd-china.com/topic/1992/cyclic%E5%91%A8%E6%9C%9F%E6%80%A7%E8%BE%B9%E7%95%8C%E6%9D%A1%E4%BB%B6/6
[2] : https://openfoam.org/release/2-2-0/boundary-conditions/
[3] : https://www.cfd-china.com/topic/2121/q-dns%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%A7%BD%E9%81%93%E6%B5%81%E9%81%87%E5%88%B0%E4%BA%86%E4%B8%80%E4%BA%9B%E9%97%AE%E9%A2%98-%E6%B1%82%E5%A4%A7%E7%A5%9E%E4%BB%AC%E6%8C%87%E7%82%B9
[4] : https://blog.csdn.net/CloudBird07/article/details/105102079
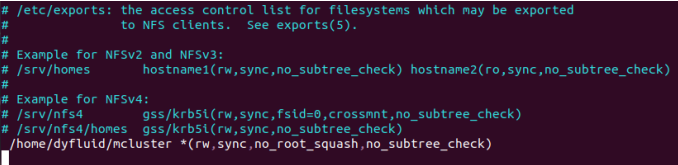
1.设置周期型边界条件需要使用cyclic边界条件并指定cyclic边界条件的类型,利用snappyHexMesh生成网格以及边界后进入ployMesh文件夹中编辑boundary文件,将想要设置为周期性边界条件的边界设置为cyclic并设置好他们的相邻边界,这里值得一提的是需要放大matchToTolerance的值方便之后createPatch的设定
7
(
wall1
{
type wall;
inGroups 1(wall);
nFaces 8232;
startFace 9475455;
}
wall2
{
type cyclic;
inGroups 1(cyclic);
nFaces 8232;
startFace 9483687;
//matchTolerance 1000;
transform none;
neighbourPatch wall3;
}
wall3
{
type cyclic;
inGroups 1(cyclic);
nFaces 8232;
startFace 9491919;
// matchTolerance 1000;
transform none;
neighbourPatch wall2;
}
wall4
{
type wall;
inGroups 1(wall);
nFaces 8232;
startFace 9500151;
}
wall5
{
type cyclic;
inGroups 1(cyclic);
nFaces 34548;
startFace 9508383;
// matchTolerance 1000;
transform none;
neighbourPatch wall6;
}
wall6
{
type cyclic;
inGroups 1(cyclic);
nFaces 34548;
startFace 9542931;
//matchTolerance 1000;
transform none;
neighbourPatch wall5;
}
BALL
{
type wall;
inGroups 1(wall);
nFaces 152712;
startFace 9577479;
}
)
下一步就是建立createPatchDict文件对周期性边界条件进行设置
// with transformations (i.e. cyclics).
pointSync false;
// Optional: Write cyclic matches into .obj format; defaults to false.
writeCyclicMatch false;
// Patches to create.
patches
(
{
// Name of new patch
name wall2;
// Dictionary to construct new patch from
patchInfo
{
type cyclic;
neighbourPatch wall3;
// Optional: explicitly set transformation tensor.
// Used when matching and synchronising points.
//transform rotational;
//rotationAxis (1 0 0);
//rotationCentre (0 0 0);
// transform translational;
// separationVector (1 0 0);
// Optional non-default tolerance to be able to define cyclics
// on bad meshes
// matchTolerance 1E-2;
}
// How to construct: either from 'patches' or 'set'
constructFrom patches;
// If constructFrom = patches : names of patches. Wildcards allowed.
patches (wall2);
// If constructFrom = set : name of faceSet
//set f0;
}
{
// Name of new patch
name wall5;
// Dictionary to construct new patch from
patchInfo
{
type cyclic;
neighbourPatch wall6;
// Optional: explicitly set transformation tensor.
// Used when matching and synchronising points.
//transform rotational;
//rotationAxis (1 0 0);
//rotationCentre (0 0 0);
// transform translational;
// separationVector (1 0 0);
}
// How to construct: either from 'patches' or 'set'
constructFrom patches;
// If constructFrom = patches : names of patches. Wildcards allowed.
patches (wall5);
// If constructFrom = set : name of faceSet
//set f0;
}
);
注意此处有坑:设置patch的边界一定要设置为你在boundary文件里最先设置为cyclic的边界。
执行creatPatch与checkMesh命令实现周期性边界条件设置。
2.of中周期性边界条件的压力梯度实现有两种方法:
一种是在初始边界条件上运用fixedJump方法,设置两个边界的压差实现压力梯度驱动,这种方法最为简单。
inlet
{
type fixedJump;
patchType cyclic;
jump uniform -151;
value $internalField;
}
outlet
{
type fixedJump;
patchType cyclic;
value $internalField;
}
另外一种方法是对动量方程实现修改,添加一个压力梯度的源项,其实现方法如下:
(1)首先定义一个基于原求解器的自定义求解器,方法详见: https://www.bilibili.com/video/av75230449/
在creatFields文件中添加压力梯度场:
volVectorField pGrad
(
IOobject
(
"pGrad",
runTime.timeName(),
mesh,
//IOobject::MUST_READ,
IOobject::NO_READ,
IOobject::AUTO_WRITE
),
mesh,
//Zero
//vector(500, 0, 0)
dimensionedVector("pGrad",dimensionSet(1, -2, -2, 0, 0),vector(-500,0,0))
);
此处值得注意的是定义的场为矢量场,且他的单位应该是压力梯度的单位,这里设置它的数值为x方向的-500;
之后在UEqn.H求解动量方程文件中添加源项:
MRF.correctBoundaryVelocity(U);
fvVectorMatrix UEqn
(
fvm::ddt(rho, U) + fvm::div(rhoPhi, U)
+ MRF.DDt(rho, U)
+ turbulence->divDevRhoReff(rho, U)
+ fvm::Sp(rho*coupling.damping(), U)
+ fvm::Su(rho*coupling.source(), U)
==
fvOptions(rho, U)-pGrad
);
UEqn.relax();
实现之后执行wmake进行重新编译就可实现每个网格上均匀压力梯度驱动的求解器了
3.那么同样是体积力,在设置重力文件中添加数值是否和以上添加压力梯度的方法起到一样的效果呢,答案是否定的:
fvOptions.constrain(UEqn);
if (pimple.momentumPredictor())
{
solve
(
UEqn
==
fvc::reconstruct
(
(
mixture.surfaceTensionForce()
- ghf*fvc::snGrad(rho)
- fvc::snGrad(p_rgh)
) * mesh.magSf()
)
);
fvOptions.correct(U);
}
我们可以看到方程中重力项的实现是- ghf*fvc::snGrad(rho),ghf定义如下:
new surfaceScalarField
(
"ghf",
(gFluid[i] & fluidRegions[i].Cf()) - ghRef
)
其中gFluid[i]返回了通过字典(constant/g)读取得到的重力加速度项,fluidRegions[i].Cf()返回了当前网格表面的面心矢量,ghRef是给定的相对重力加速度,一般为0。综上所述,openFOAM中的重力的表达式为:$\vec{G}=-(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s}) \nabla \rho$
其中$\vec{S}$是待求点的位置矢量,这显然与方程1使用的重力表达式相差很大,接下来我们就一步一步推导这个结果。
首先明确,在涉及到重力的求解器中,其求解的压力p并不是总压P,而是动压,即:$P=p+\rho \vec{g} \cdot \vec{s}$
之所以要这样处理是为了方便用户设置初场,大家可以设想最简单的溃坝算例,如果直接对总压设置初场,那我们要设置的则是一个梯形的压力分布,计算域的y坐标越高其净水压强就越大,而如果我们拆分成动压和静压的形式,就可以直接设置初场为0了。在动量方程中,我们存在对总压的压力梯度项,将总压拆成静压和动压即可得到:
$\nabla P=\nabla(p+\rho \vec{g} \cdot \vec{s})=\nabla p+\nabla(\rho \vec{g} \cdot \vec{s})=\nabla p+(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s}) \nabla \rho+\rho \nabla(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s})$
$\nabla(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s})=\nabla(g y)=\left(\frac{\partial(g y)}{\partial x}, \frac{\partial(g y)}{\partial y}, \frac{\partial(g y)}{\partial z}\right)=(0, g, 0)=\vec{g}$
$\nabla P=\nabla p+(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s}) \nabla \rho+\rho \nabla(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s})=\nabla p+(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s}) \nabla \rho+\rho \vec{g}$
得到Open foam中动量方程
$\rho \frac{\partial \vec{u}}{\partial t}+\rho \nabla(\vec{u} u)=\nabla(\mu \nabla \vec{u})-\nabla p-(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s}) \nabla \rho$
故确实是of中重力相起体积力源项的作用,但是返回的是$(\vec{g} \cdot \vec{s}) \nabla \rho$和增加压力梯度是同样的效果单位也是(1,-2,-2,0,0,0,0),但是是无法通过直接给g的数值来达到添加压力梯度的条件的。